The 3rd International Nursing and Health Sciences Students and Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP)
More infoLeadership style that can accommodate changes in uncertain times. The purpose of this study was to describe the leadership style of the head of the room in terms of the scale and construct of the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire.
MethodsThis research was a descriptive type that was conducted at the Anutapura Hospital in August 2020. There were 22 treatment rooms and the researchers took all the heads of treatment rooms to be sampled. Collecting data using a Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ-5X).
ResultsThe results showed that 63.6% tend to use transformational leadership styles, 9.1% tend to use transactional leadership styles and 27.3% are based on the leader's outcomes.
ConclusionsThe dominant transformational leadership style used by the head of the room because it is considered effective in facing the era of globalization and modernization.
The central task of leadership is to reach collective goals.1 Leadership plays an important and strategic role in an organization. leadership is like the life that determines the birth, growth, maturity and death of an organization. Leadership is very important in guarding the organization when it comes to changing erratic times.2,3 One of the challenges for a leader is to apply a leadership style that can accommodate changes in an uncertain era.
Hospital organization in its management is also determined by leadership factors. In the hospital, leadership roles range from chair and director, ward chief, operations officer, nursing and medical. Leadership by organizational managers is vital to achieving the extent of organizational change needed to reach very high levels of patient safety such as modification in management practices, workplace placement, design and workflow and organizational safety culture.4 So that all components of health workers and health support workers in the hospital understand the vital meaning of leadership.
The largest number of health workers in the hospital health service system in Indonesia are nurses with a total of 245,407 people (48.43%) of the total health personnel in hospitals of 506,725 people (100%) outside of health support personnel.5 Approximately 40–60% of services in the hospital are nursing services, this phenomenon shows that nursing services are an important part of health services in determining the success of health services.6,7
The head of the ward is the leading level leader in health services in the hospital. A very important role in ensuring that nurse members provide services. This cannot be separated from the role of the inpatient manager nurse (head of the room) in implementing his leadership style.
MethodsThis type of research is observational with descriptive characteristics and design conducted at RSU Anutapura Palu. There were 22 treatment rooms and researchers took all heads of treatment rooms to be sampled and were required to fill in informed consent. The study was conducted in August 2020. Data collection used an online questionnaire which refers to the 2009 version of the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire (MLQ) Form 5X. This questionnaire consists of 45 questions using a five-point scale ranging from (0), not at all to (4) frequent or always. There are 36 items of leadership style measures that assess transformational, transactional, and laissez-faire leadership behaviour. Nine items that measure leadership outcomes. The data were processed using descriptive analysis (frequency, percentage, mean, SD.
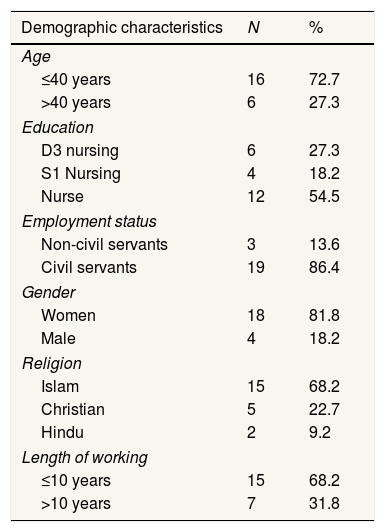
ResultDemographic characteristics of the head of the roomTwenty-two respondents are the head of the treatment room at Anutapura Hospital, Palu. The sociodemographic characteristics of the head of the room are shown in Table 1.
Respondents’ demographic details.
| Demographic characteristics | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≤40 years | 16 | 72.7 |
| >40 years | 6 | 27.3 |
| Education | ||
| D3 nursing | 6 | 27.3 |
| S1 Nursing | 4 | 18.2 |
| Nurse | 12 | 54.5 |
| Employment status | ||
| Non-civil servants | 3 | 13.6 |
| Civil servants | 19 | 86.4 |
| Gender | ||
| Women | 18 | 81.8 |
| Male | 4 | 18.2 |
| Religion | ||
| Islam | 15 | 68.2 |
| Christian | 5 | 22.7 |
| Hindu | 2 | 9.2 |
| Length of working | ||
| ≤10 years | 15 | 68.2 |
| >10 years | 7 | 31.8 |
Source: Primary Data, 2020.
Table 1 shows the dominant respondents were aged ≤40 years with the latest education as nurses. Most of the respondents are civil servants and are female, tend to be Muslim and have worked for ≤10 years.
Room head's leadership style is reviewed from the Multifactor Leadership QuestionnaireThe description of the leadership style of the head of the room at Anutapura Hospital Palu, namely 63.6% tends to use a transformational leadership style, 9.1% tend to use a transactional leadership style and 27.3% are based leader's outcomes.
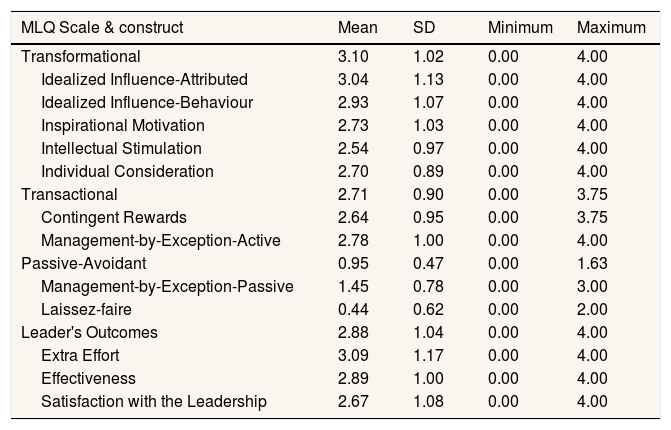
Table 2 shows the leadership style of the head of the room in terms of MLQ shows that the average head of the room quite often applies a transformational scale, sometimes applies a transactional scale and leader's outcomes, occasionally applies passive-avoidant. The constructs that are often used on a transformational scale are Idealized Influence-Attributed and Idealized Influence-Behaviour. A construct that is sometimes used on a transactional scale is Management-by-Exception-Active. The construct that is occasionally used on the passive-avoidant scale is Management-by-Exception-Passive. The construct that is often used in the leader's outcomes scale is Extra Effort.
Descriptive statistical results for leadership styles in terms of MLQ.
| MLQ Scale & construct | Mean | SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformational | 3.10 | 1.02 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Idealized Influence-Attributed | 3.04 | 1.13 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Idealized Influence-Behaviour | 2.93 | 1.07 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Inspirational Motivation | 2.73 | 1.03 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Intellectual Stimulation | 2.54 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Individual Consideration | 2.70 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Transactional | 2.71 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 3.75 |
| Contingent Rewards | 2.64 | 0.95 | 0.00 | 3.75 |
| Management-by-Exception-Active | 2.78 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Passive-Avoidant | 0.95 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 1.63 |
| Management-by-Exception-Passive | 1.45 | 0.78 | 0.00 | 3.00 |
| Laissez-faire | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 2.00 |
| Leader's Outcomes | 2.88 | 1.04 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Extra Effort | 3.09 | 1.17 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Effectiveness | 2.89 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
| Satisfaction with the Leadership | 2.67 | 1.08 | 0.00 | 4.00 |
M, mean; SD, standard deviation; MLQ, Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire.
Leadership style from Bass and Avolio (1996) state that there are three types of leadership styles, namely transactional leadership styles, transformational leadership styles, and passive-avoidant leadership styles.7 The number of studies that have been done proves that the favourite leadership style adopted is the transformational leadership style.8 It is obtained that the description of room head's leadership style at the Anutapura Hospital Palu, namely 63.6%, tends to use a transformational leadership style. The factor that influences the implementation of patient safety measures is the leadership of the head of the room.9
Transformational leadership that has a vision of the future, is able to see changes in the organizational environment, provides motivation and inspiration for its members. Leaders and their members are able to control the organization, through the implementation of performance management that is responsible, creative, innovative, solid and has a good work ethic.10 Transformational leadership motivates their subordinates to perform above and beyond their call of duty.11 It can be concluded that transformational leadership is a leadership style through a process of increasing aspirations, inspiration and motivation, having a vision for the future and being able to identify environmental changes and transform extraordinary changes into an organization so that the individual members who are coordinated grow a high sense of trust which is capable encouraging to build a solid team and contribute more to the organization.
Four dimensions make up transformational leadership, namely intellectual stimulation, individual consideration, inspirational motivation, and idealized influence. The dimension of intellectual stimulation stimulates subordinates to always be creative and innovative. The next dimension is individualized consideration, which is being able to understand the individual differences of his subordinates more deeply by hearing their aspirations, educating and training subordinates. From here, transformational leaders can see the potentials that exist and the development of their subordinates and facilitate them. Next is inspirational motivation, which is the character of a leader who can apply high standards to generate a spirit of optimism and high enthusiasm from his subordinates. Lastly, idealized influence dimension that sees the charisma of a leader to have a strong influence and high self-confidence and looks at the actions of a charismatic leader such as the values that are carried.12 The dimensions of transformational leadership style show that a leader must be a role model for his subordinates.
Research by Alloubani et al. (2015) explains that there is a positive relationship between transformational leadership style and behaviour with organizational consequences such as leader effectiveness, job satisfaction and employee readiness to make additional efforts.8
The most important contribution in the creation of transformational leadership is reflected in the ability of leaders to be able to influence the ideal qualities of transformational leaders to become an inspiration for followers and create valuable values and concepts in individuals and leaders understand the needs of growing followers and to meet these needs and nurture individuals, will apply a coaching style (individual considerations) until the creation of employee performance and job satisfaction that is felt by employees increases. Permanent emotional intelligence officers are proven to improve employee performance but not the job satisfaction felt by employees.13
In addition to the transformational leadership style, 9.1% of the ward heads at Anutapura Hospital Palu used a transactional leadership style. Marselius ST and Rita Andarika (2004) in their research found that there is a positive relationship between perceptions of transformational and transactional leadership styles together with a very significant impact on job satisfaction.14 The styles most often adopted by leaders are transformational and transactional leadership styles, while the styles most often adopted by leaders are transformational and transactional leadership styles. Passive-avoidant is not a favourite.15 This passive-avoidant leadership style, a leader tends to let go of responsibility and to maintain overall distance from a problem faced by his subordinates. If there is an error or failure committed by the innate in the process of achieving goals, the leader will give warnings and sanctions to the subordinates concerned. However, if in the achievement process there is no failure or error whatsoever and goes according to the established standards and procedures, then the leader does not provide any evaluation to his subordinates.16
ConclusionFrom this research, it can be concluded that the leadership style of the head of the room in terms of the scale and construct of the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire the most dominant are transformational and transactional styles. The influence of transformational leadership which includes inspirational motivational charismatic intellectual stimulation and individual attention and transactional dimensions which include contingent rework and management by exception on employee performance as measured by this study provide support for the influence of almost all dimensions of transformational and transactional leadership.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 3rd International Nursing, Health Science Students & Health Care Professionals Conference. Full-text and the content of it is under responsibility of authors of the article.