The 3rd International Nursing and Health Sciences Students and Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP)
Más datosThis research was aimed to develop and test virtual reality-based learning media in improving active management skills of the third stage labor in midwifery students.
MethodsThis study uses a Research and Development (R&D) research design method developed by Borg and Gall. The stages of this study consisted of; analysis of the needs of virtual reality-based learning media about active management of the third stage, planning of the development of instructional media development, development of instructional media, expert validation, one-on-one trials, small group trials, large group trials, and the final product of learning media.
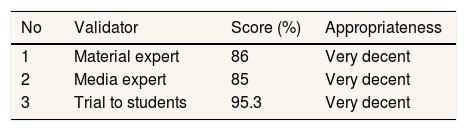
ResultsThe percentage of instructional media assessment using questionnaires in the expert validation test and large group trials in this study showed the calculation of the results of the learning media rating according to material experts (86%) category is very feasible, according to media experts scored (85%) very feasible. The results of trials to students score (95.3%) so that virtual reality-based learning media about active management of the third stage made are very feasible to be used as learning media for midwifery students in the active management skills of students the third stage.
ConclusionVirtual reality-based learning media about active management of the third stage labor are designed according to the needs of lecturers and students with additional features of bleeding warning, anatomy of placental physiology and are declared to be very suitable for use as learning media for midwifery students.
Learning media in midwifery is one of the tools or physical means used in the teaching and learning process to provide convenience. In midwifery education, students need to improve clinical skills and practice simulation before the practice curve directly to patients. This can reduce errors in providing midwifery care. So that in the development of education, learning media can improve clinical skills that are more practical and can be seen continuously. Learning media is expected to be used to overcome various problems in the teaching and learning process, especially on internal problems such as student and teacher attitudes, outlook on life, pleasure, and feelings, not happiness.1,2
Virtual reality is a virtual simulation usually characterized by its immersive nature, 3-dimensional characteristics, motion sensors, and devices haptic which applies the sensation of touch to human interaction with computers. This VR technology can present an artificial world and try things that are not accessible in real life and present them in the user's view. Virtual reality also offers an interactive environment that involves students and allows students to visualize it.3,4
Research conducted in Italy, VR is being developed for use as a medium for learning and stimulating blood vessel anatomy and physiology. Likewise, by using virtual patients, students can interactively practice honing skills such as effective communication, psychiatric interviews, and emergency simulations. Display interfaces that look real in a VR environment can help users focus on learning objectives rather than learning with a computer screen vulnerable to distraction with other learning resources, such as opening web pages or books.5
MethodResearch sitesThis research was conducted in the period May–June 2020 conducted at the STIKes Salewangan Maros Campus. In this study, stages are consisting of; analysis of the needs of virtual reality-based learning media about active management of the third stage, planning of instructional media development design, development of instructional media, expert validation, one-on-one trials, small group trials, large group trials, and the final product of learning media.6
Research stages- 1.
Analysis of the needs of virtual reality-based learning media about active management in the third stage.7
Researchers conducted a preliminary survey in several campus locations in Makassar and outside the city of Makassar related to problems that occur in the skills of semester IV students and found a lack of students’ ability to carry out practical management skills in the third stage. At this stage, the researcher gets the results of a survey of what happened at the Salwengan Maros STIKes by conducting interviews with lecturers and students about the third stage's active management skills, which is still lacking.
- 2.
Design planning for developing virtual reality-based learning media about active management in the third stage
After analyzing the problems and needs of students, the basic competencies that will be developed in the learning media are determined. Researchers designed the design and features that will be displayed on virtual reality learning media by using book guidelines and literature on the third stage of childbirth care accompanied by the help of experts in information technology.
- 3.
Development of virtual reality-based learning media about active management in the third stage
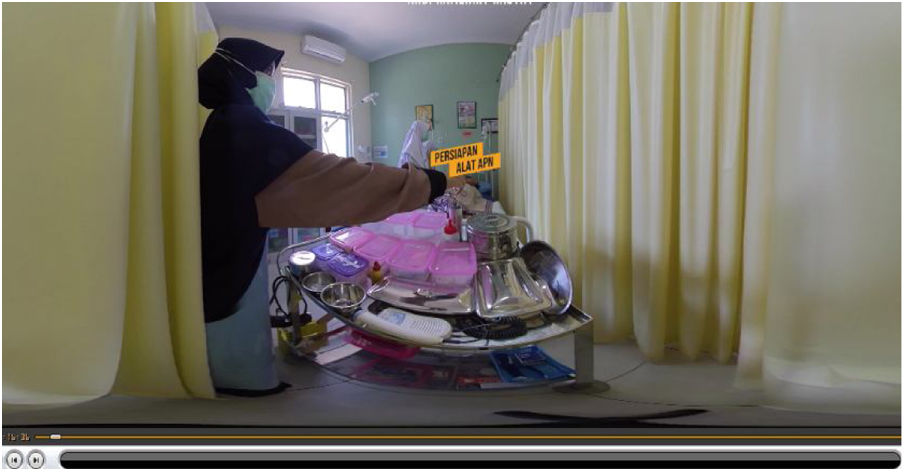
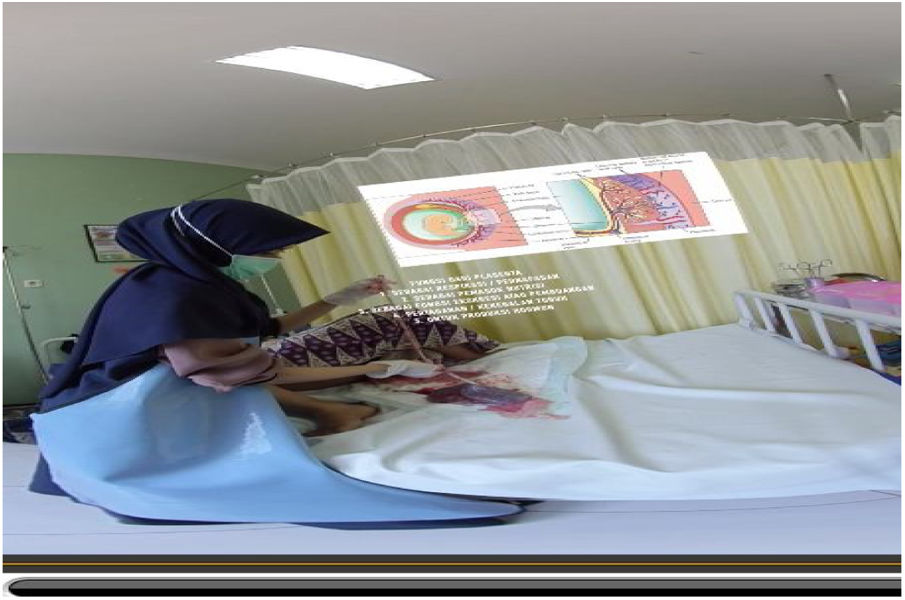
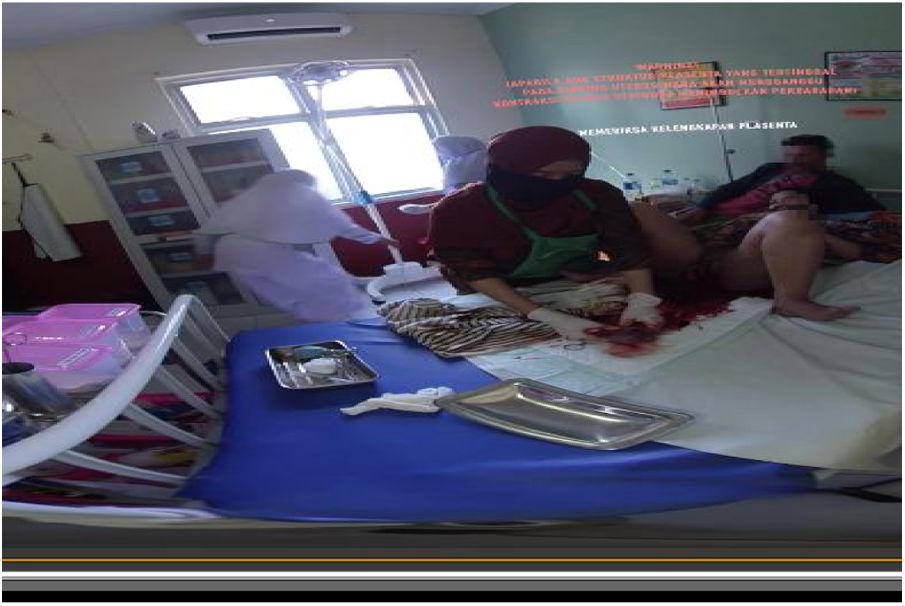
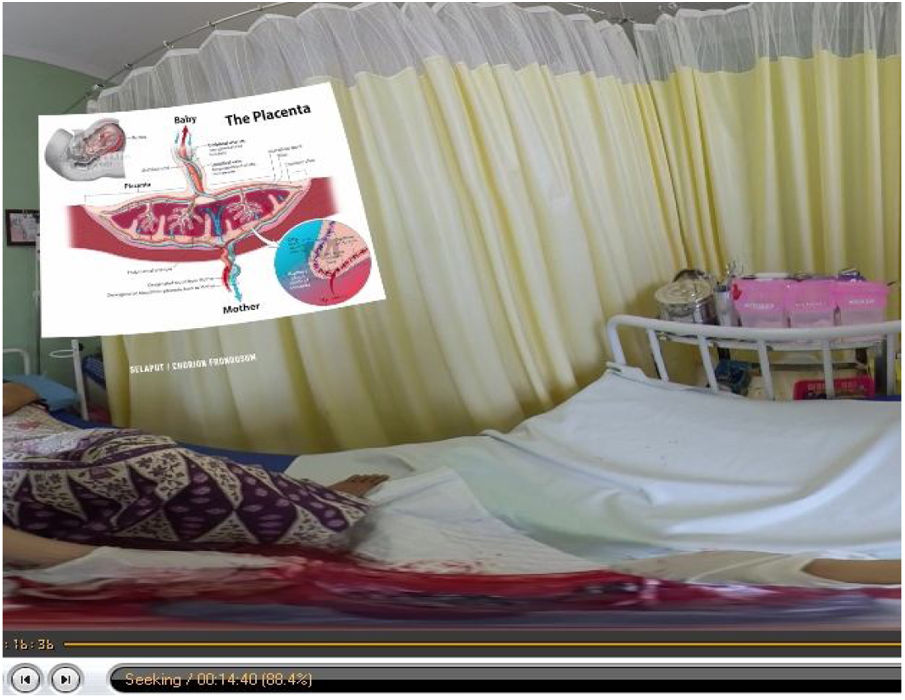
At this stage, the researchers developed the learning media using virtual reality containing the steps of the third stage of active management that were developed in real video 360 and can be viewed in 3D by adding warning features and additional material in the anatomy and physiology of the placenta, including writing, explanatory audio and multiple-image display.
- 4.
Expert validation
The researcher conducted a validation consisting of 4 experts, namely 1 Media Expert and 3 Material Expert in virtual reality-based learning media about active management in the third stage. The material expert validation questionnaire and IT expert validation were adopted from the questionnaire that was used in the study Aziz in 2015.
- 5.
One-on-one trial
They were conducting one-on-one trials with midwifery lecturers who took 3 Askeb II (Childbirth) courses to get input on explanations of material, steps in the management checklist stage III, features, and designs on the media by filling out questionnaires.
- 6.
Small group trial
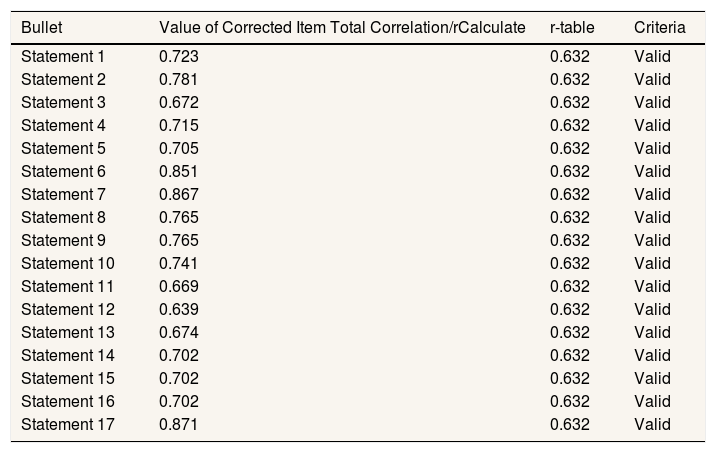
By conducting a small group trial with ten students, virtual reality-based learning media were provided, and questionnaire validation was conducted by filling out questionnaires related to the function of VR-based learning media. The validity test results are used with the results in Table 1.
Table 1.Validity test results.
Bullet Value of Corrected Item Total Correlation/rCalculate r-table Criteria Statement 1 0.723 0.632 Valid Statement 2 0.781 0.632 Valid Statement 3 0.672 0.632 Valid Statement 4 0.715 0.632 Valid Statement 5 0.705 0.632 Valid Statement 6 0.851 0.632 Valid Statement 7 0.867 0.632 Valid Statement 8 0.765 0.632 Valid Statement 9 0.765 0.632 Valid Statement 10 0.741 0.632 Valid Statement 11 0.669 0.632 Valid Statement 12 0.639 0.632 Valid Statement 13 0.674 0.632 Valid Statement 14 0.702 0.632 Valid Statement 15 0.702 0.632 Valid Statement 16 0.702 0.632 Valid Statement 17 0.871 0.632 Valid Source: Primary Data.
Based on Table 1, it can be seen that all statements can be declared valid because of the Corrected Item Total Correlation/rCount> r-table.
- 7.
Large group trials
Conducting a large group trial with 30 student intervention groups given a virtual reality-based learning media then taking questionnaires that have been validated.
- 8.
The final product of virtual reality-based learning media about active management in the third stage
A VR-based learning media product was born at this stage, which had undergone a development stage to produce the third childbirth care learning media. Students use this media as a tool in the learning process that is flexible, interesting so that it can trigger student motivation to improve their skills (Figs. 1–4).
Virtual reality-based learning media is tested for validity by stages 4 and 7 of the study. Table 2 shows the calculation of the results of the learning media rating according to material experts (86%), according to the media experts scored (85%), and the results of trials to students scored (95.3%). It can be concluded that the learning media is based on virtual reality about the active management of the third stage is very suitable to be used as one of the learning media in child care courses.
DiscussionDevelopment of instructional media with virtual simulations Active Management, the third stage labor, provides the best teaching and learning systems solution today. This learning media contains information about proper and directed newborn care. MAK III is fast and precise, monitoring bleeding and early detection of danger signs at stage III. The VR learning media was created with the aim to improve active management care skills on stage III and danger signs on stage III.
Virtual reality is an innovative tool for solving complex problems to produce unique, realistic, and practical solutions for students.3,4 This study is in line with research conducted by Fealy et al. Said that learning media based on Virtual Reality has the potential to increase competence and confidence for students who provide learning opportunities that can be re-accessed, seen directly, and provide opportunities for educators to provide creative or easily understood learning designs or media.4,8
Research conducted found a positive correlation in the presence of students in class conceptual material learning with Virtual Reality learning media that will increase the willingness and inspiration for students to learn.9
This research is in line with the study of Williams, 2018 that by using Virtual Reality-based learning media, has gained recognition in terms of increasing risk-free knowledge and skills and minimizing direct practice errors made by students during the Neonatal Resuscitation learning process. There are many benefits in Virtual Reality learning media, especially in education that can be used as a multi-modal to teach neonatal resuscitation practicum.10
The expert validation test and large group trials in this study showed the calculation of the results of the learning media rating according to material experts (86%) are very feasible, according to media experts score (85%) is very feasible. The test results to students get a value (95, 3%) so that the VR-based learning media about active management of the third stage that has been made is very feasible to be used as a medium for learning midwifery students in childbirth care subjects especially in the learning of childbirth care in the third stage. This research is in line with Mahardika's research, 2016 Learning media using Virtual Reality have the potential as a viable learning media and can facilitate students in pre-clinical and clinical learning in the medical world.
This study is in line with the research of Massetti, 2018 who found that the use of VR media has a good effect on the development of learning and increases knowledge in the rehabilitation of neuron nerves, identification of cerebral palsy patients, spinal cord injuries, and post-stroke management.11 The responses given by students and teachers before and after the teaching and learning process using learning media give a positive impression to increase motivation and interest in learning.12
Virtual Reality application is very convenient to use in the teaching and learning process in clinical and health services. This application has enormous opportunities in medical and academic midwives. Virtual reality provides data presentation that combines the real world and the virtual world so that it makes it easier for students to see and recognize firsthand events that have never been seen before.13
ConclusionThis study concludes that the virtual reality-based learning media about active management of the third stage is designed according to the needs of lecturers and students. There are videos on newborn care, active management of the third stage, and bleeding monitoring that can be seen in 3D, and there are additional features of bleeding warning, anatomy, and placental physiology that can increase student interest in learning. This media is declared very feasible to be used as a medium for learning midwifery students in childbirth care courses, especially in active management learning at the third stage.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the 3rd International Nursing, Health Science Students & Health Care Professionals Conference.